When to Seek Medical Attention for a Concussion
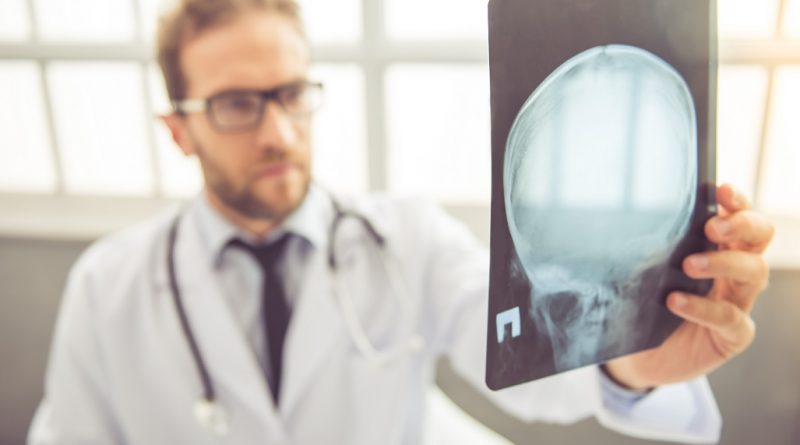
A concussion is a traumatic brain injury.
A blow to your head or violent shaking of your head and upper body can cause concussions. When that happens, your brain can forcefully slide back and forth against your skull’s inner walls. In turn, that can affect your brain function.
Often, that only happens for a brief time and you could experience temporary effects like headaches and problems with balance, coordination, concentration, and memory.
Corporate Wellness App
CircleCare
Other times, the symptoms of concussions can be more severe and require urgent medical care.
So, let us take a look at when you should seek medical attention for a concussion.
You Should Actually Always See a Doctor After a Concussion
There are times when you should seek urgent medical attention for a concussion, as we shall see. But you should actually always make an appointment to see your doctor within one to two days after experiencing a head injury, even if there are no noticeable symptoms.
And sometimes, signs and symptoms do not show up until days after the injury.
Your doctor will evaluate you, review your medical history, and could perform a neurological examination, imaging tests, and cognitive tests.
Also, it could be worthwhile visiting a clinic that specializes in concussions, especially if you have persistent signs and symptoms after the injury.
The physicians, therapists, and specialists at a professional concussion clinic, such as the Neural Effects clinic, can help you recover more quickly.
When to Seek Emergency Medical Attention
In some situations, you should call 911 or get to an Emergency Room straight away after experiencing a concussion.
In rare cases, a concussion could cause you to develop a blood clot that presses the brain against the skull.
Therefore, it is vital that you get emergency medical attention if there are any danger signs after a concussion.
Those danger signs include:
- A persistent headache that worsens or does not go away.
- Repeated vomiting.
- Slurred speech.
- Weakness.
- Numbness.
- Convulsions or seizures.
- Decreased coordination.
- One pupil that is larger than the other.
- Difficulty recognizing people or places.
- A loss of consciousness.
Danger Signs in Children
If your child experiences a concussion via a bump, blow, or jolt to the head, and has any of the above symptoms, you should seek emergency medical attention straight away. You should also seek immediate medical attention if your child will not stop crying and is inconsolable or will not eat.
If your child moves normally, remains alert, and responds to you, the injury is probably mild and does not require urgent care.
But, as mentioned above, it is always recommended that a doctor is consulted within one or two days after any type of injury that involves a concussion, even if the concussion is mild.
Potential Complications
Sometimes, complications can arise after a concussion, which is just one reason why you should see a doctor after experiencing a blow or jolt to the head.
Complications include things like:
- Post-traumatic headaches.
- Post-traumatic vertigo.
- Second impact syndrome.
- Persistent post-concussive symptoms.
Risk Factors
It is worth being aware of potential risk factors for concussions. You can then take preventive measures or at the very least, take more care.
Factors and activities that can potentially increase the risk of a concussion include:
- Participating in high-risk contact sports like football, boxing, soccer, and hockey.
- Falling, particularly in young children and older adults.
- Being involved in a motor vehicle accident.
- Being involved in a bicycle or pedestrian accident.
- Being a victim of physical abuse.
- Being a soldier who is involved in combat.